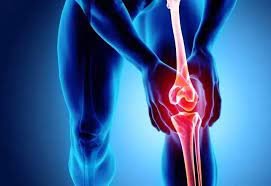
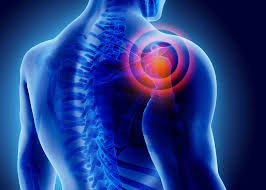
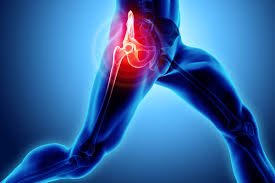
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic Surgery
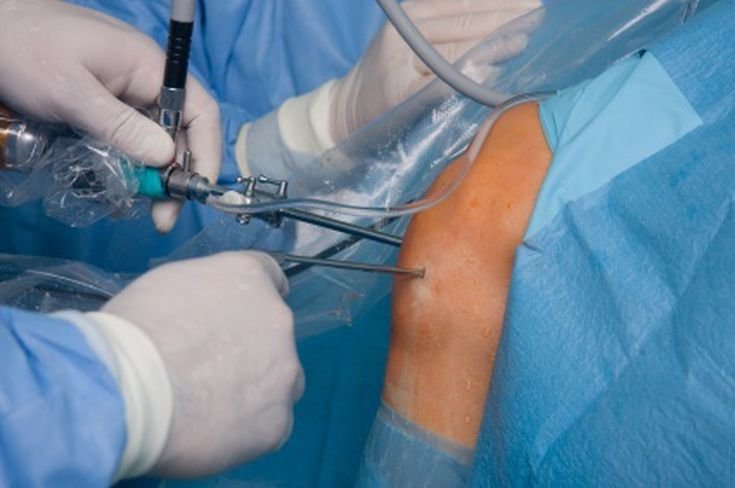
What is Arthroscopic Surgery?
Joints Commonly Treated with Arthroscopy:
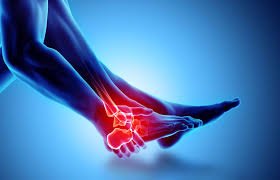
Ankle
The ankle is a joint connecting the foot and the lower leg, also referring to the area surrounding this joint.
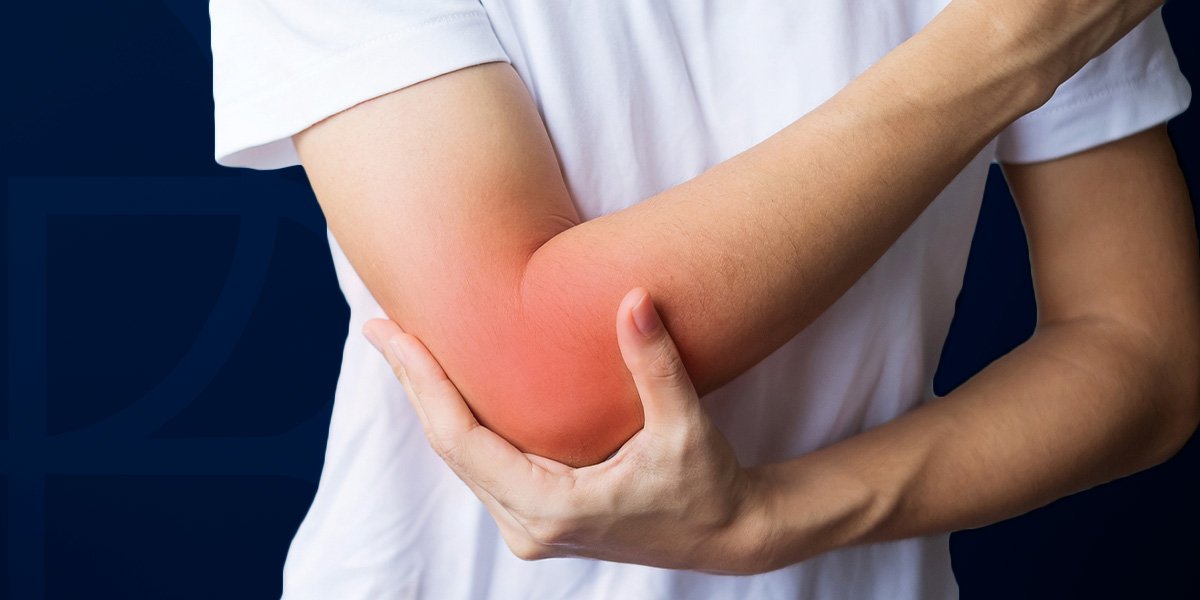
Elbow
Apipe fitting used in plumbing systems to connect two pipes of the same or different nominal diameter.
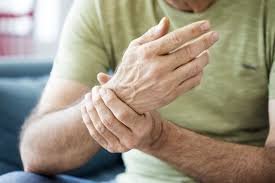
Wrist
a joint that connects the hand to the forearm, allowing for a wide range of hand movements.
Benefits of Arthroscopic Surgery
Smaller incisions, less pain
Faster recovery and return to activities
Minimal scarring
Lower risk of infection
Shorter downtime compared to traditional open surgery
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Most patients experience only mild to moderate discomfort. Pain is much less compared to traditional open surgery and is easily managed with medications.
Recovery varies by joint and procedure. Minor procedures can recover in 2–3 weeks, while more complex repairs (like ACL reconstruction) may take 3–6 months.
Yes. Rehabilitation is a crucial part of recovery. Physical therapy helps restore strength, flexibility, and joint mobility.
As with any surgery, risks include infection, blood clots, or joint stiffness. However, arthroscopy has a low complication rate.
Depending on your activity level and type of surgery, you may return to light work within 1–2 weeks and sports within 4–12 weeks, as advised by your surgeon.