Meniscal Repair
Meniscal Repair
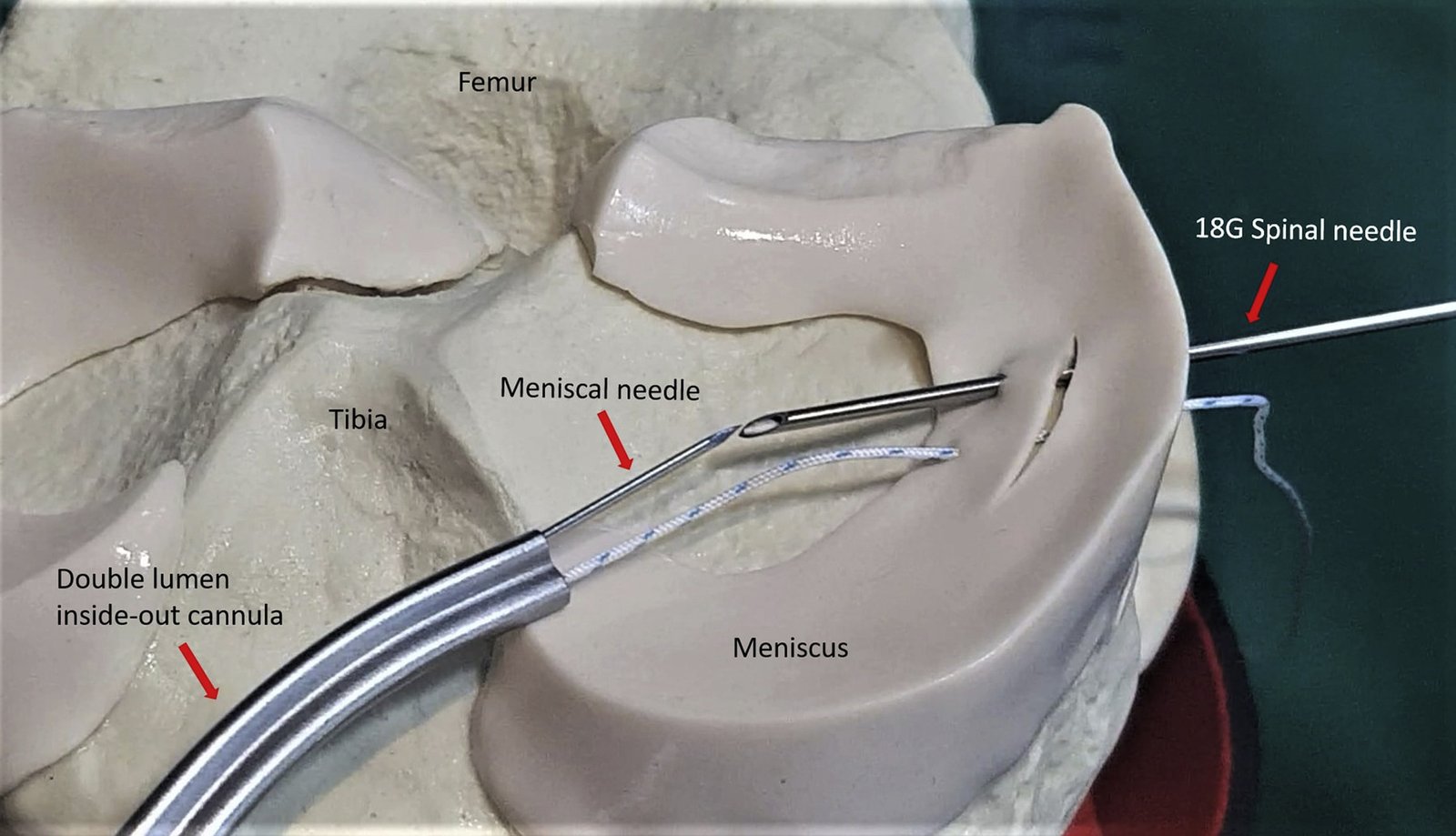
Our Meniscal Treatment Approach
Diagnosis
Clinical examination (McMurray’s test, joint line tenderness)
MRI scan to evaluate tear type, size, and location
2. Treatment Options
Non-Surgical:
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE)
Anti-inflammatory medications
Physical therapy
Surgical:
Meniscal Repair (Preserving the Meniscus):
Arthroscopic procedure using sutures or anchors
Suitable for tears in the outer (red-red or red-white) zone
Partial Meniscectomy (Trimming the Meniscus):
Only the damaged portion is removed
Performed when the tear is in a non-healing zone (white-white zone)
Meniscal Repair Surgery: What to Expect
Performed under regional or general anesthesia
Minimally invasive (arthroscopic)
Small incisions with quick recovery
Same-day discharge in most cases
Rehabilitation begins within days
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, when feasible. Meniscal repair preserves the natural cartilage, reducing the risk of early arthritis and maintaining knee function better in the long term.
No. Only tears in the vascular zones (outer part) have the potential to heal after repair. Complex or degenerative tears may require partial meniscectomy instead.
Typically between 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity and whether other knee issues (e.g., ACL tear) are being addressed simultaneously.
Most patients use crutches for 2 to 4 weeks. Weight-bearing is gradually allowed depending on the tear location and surgeon’s recommendation.
Post-operative discomfort is common but manageable with pain medications, rest, and ice therapy. Pain reduces significantly within the first two weeks.

